Forest-based solutions for sustainable farming: Unlocking Ecosystem Services for Prosperity
Forests, often referred to as nature’s lungs, are emerging as key contributors to sustainable agriculture through innovative forest-based solutions.
These solutions leverage the inherent ecosystem services provided by forests to address the challenges faced by agriculture in the modern era.
Understanding and implementing these strategies can pave the way for a harmonious coexistence between agriculture and the environment.
Forest Based Solutions as Key Contributor to Sustainable Agriculture
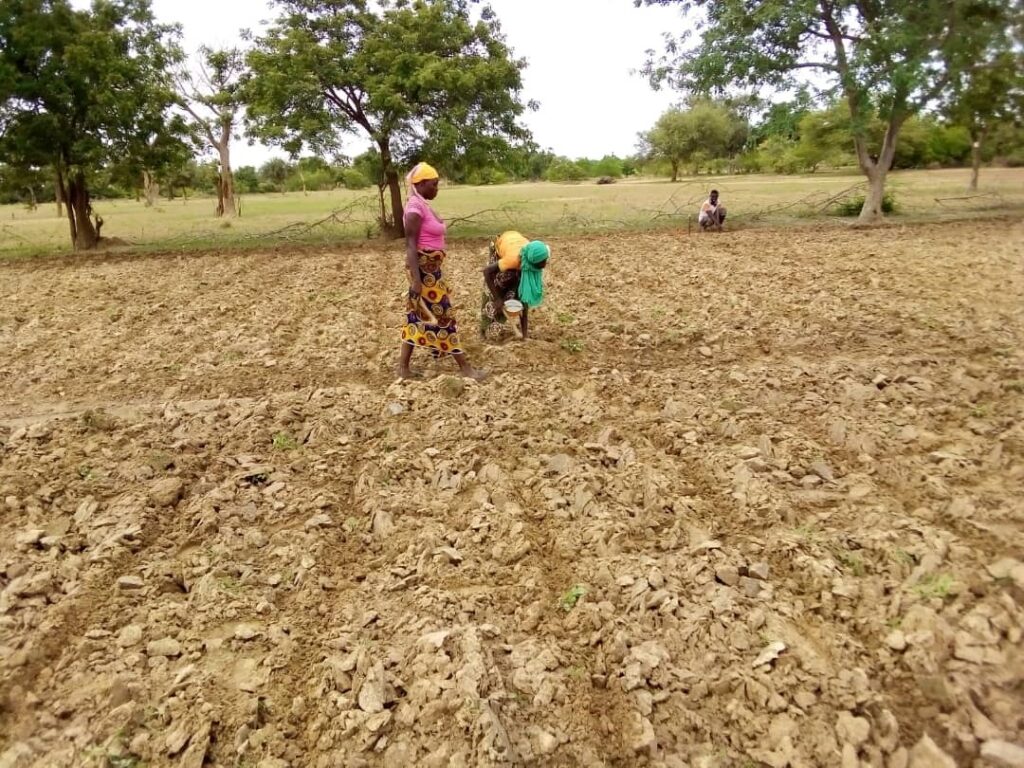

Agroforestry, a prominent forest-based solution, involves integrating trees and shrubs into agricultural landscapes.
This practice not only enhances biodiversity but also contributes to improved soil health.
The canopy cover provided by trees helps regulate temperature, reducing the impact of extreme weather conditions on crops.
Moreover, the organic matter from trees enriches the soil, fostering increased fertility and resilience.
In the realm of biodiversity conservation, forest-based solutions play a pivotal role. By establishing buffer zones and wildlife corridors between agricultural lands and forests, we can facilitate the movement of species critical for natural pest control.
This integrated approach minimizes the need for chemical pesticides, promoting a healthier environment for both crops and the surrounding ecosystem.
The concept of forest-based water regulation is paramount for sustainable agriculture. Forests act as natural sponges, absorbing excess rainwater during storms and releasing it gradually during dry periods.
This regulation helps prevent soil erosion, safeguarding valuable topsoil in agricultural fields.
Implementing forest-based water management practices ensures a stable and sustainable water supply for crops, mitigating the impact of droughts and floods.
Addressing the global challenge of climate change, forest-based solutions contribute significantly to carbon sequestration.
Trees absorb carbon dioxide, a major greenhouse gas, during photosynthesis, mitigating the effects of climate change.
Sustainable forestry practices, such as reforestation and afforestation, not only sequester carbon but also enhance the overall climate resilience of agricultural ecosystems.
In the context of soil health and fertility, forest-based solutions promote a holistic approach to land management.
The presence of trees improves soil structure, prevents erosion, and enhances nutrient cycling.
Agroforestry systems, where trees and crops coexist, create a dynamic environment that fosters long-term soil health, reducing the reliance on synthetic fertilizers.
Role of Forests in Providing Ecosystem Services
Forests play a crucial role in providing a wide range of ecosystem services, and their significance in promoting sustainable agriculture cannot be overstated.
Ecosystem services are the various benefits that humans derive from the natural environment, and forests contribute significantly to the provision of these services.
In the context of sustainable agriculture, forests offer a multitude of benefits that contribute to the well-being of both the environment and society.

- Biodiversity Conservation: Forests are home to a staggering variety of plant and animal species, making them reservoirs of biodiversity. Biodiversity is essential for maintaining resilient ecosystems and is directly linked to agricultural productivity. The diverse array of organisms in forests contributes to natural pest control, pollination of crops, and overall ecosystem stability.
- Water Regulation: Forests act as natural water regulators by influencing local and regional hydrological cycles. Tree roots help absorb excess water during periods of heavy rainfall, preventing soil erosion and flooding. During drier periods, forests release stored water, maintaining stream flow and supporting agricultural activities downstream. This regulation is crucial for sustaining water resources for both crops and livestock.
- Climate Regulation: Forests play a pivotal role in climate regulation by sequestering carbon dioxide through the process of photosynthesis. The preservation and expansion of forests contribute to mitigating climate change by acting as carbon sinks. Stable climatic conditions are vital for agriculture, and healthy forests play a role in regulating temperature, precipitation patterns, and overall climate resilience.
- Soil Health and Fertility: The presence of trees in and around agricultural landscapes enhances soil health. Trees contribute organic matter to the soil through the shedding of leaves and other plant debris. This organic matter improves soil structure, water retention, and nutrient content. Additionally, the intricate root systems of trees prevent soil erosion, reducing the risk of nutrient loss from agricultural fields.
- Pollination Services: Forests are crucial for supporting pollinators, such as bees and butterflies, which play a fundamental role in the pollination of crops. Many agricultural crops depend on these pollinators for reproduction. The proximity of forests to agricultural areas provides a habitat for pollinators, ensuring the continued pollination of crops and, consequently, higher yields.
- Cultural and Recreational Values: Forests offer cultural and recreational values that contribute to the overall well-being of communities. The aesthetic and spiritual aspects of forests have a positive impact on mental health. Additionally, forests provide opportunities for eco-tourism, creating economic benefits for local communities and fostering a sense of stewardship for the environment.
- Timber and Non-timber Forest Products: Sustainable forestry practices can provide a renewable source of timber and non-timber forest products. These resources can be vital for local economies and can contribute to the development of sustainable and diversified agricultural practices.
The role of forests in providing ecosystem services is integral to the promotion of sustainable agriculture.
Recognizing the interconnectedness between forests and agricultural systems is essential for developing practices that balance human needs with environmental conservation.
Sustainable land management strategies should prioritize the preservation and restoration of forests, ensuring their continued contribution to the well-being of ecosystems and societies alike.
Unlocking Profitability: Forest-Based Solutions and the Lucrative Landscape of Ecosystem Services
The adoption of forest-based solutions not only aligns with environmental stewardship but also holds significant promise for profitability within the realm of providing ecosystem services.
As businesses and communities increasingly recognize the value of sustainable practices.
Investing in forest-based solutions can lead to a host of economic benefits while ensuring the longevity of vital ecosystem services.
One of the key avenues for profitability lies in the cultivation of non-timber forest products (NTFPs).

Forests are rich reservoirs of diverse products such as medicinal plants, fruits, nuts, and resins.
By sustainably harvesting and marketing these products, communities can generate income streams that are not only economically viable but also environmentally sustainable.
This approach promotes a balance between meeting economic needs and preserving the integrity of the ecosystem.
Agroforestry enterprises present another avenue for profitability. Integrating trees into agricultural landscapes diversifies income sources for farmers.
Timber production, alongside crops and other forest products, contributes to a resilient and profitable agroecosystem.
The multiple revenue streams from agroforestry provide a buffer against market fluctuations, making it an attractive option for long-term economic sustainability.
Furthermore, forest-based solutions contribute to the burgeoning field of ecotourism. Preserving and showcasing the natural beauty of forests can attract tourists seeking immersive experiences in biodiverse environments.
Guided tours, wildlife watching, and recreational activities create employment opportunities and stimulate local economies.
The economic impact extends beyond the immediate community, fostering a broader appreciation for the economic value of intact ecosystems.
In the context of carbon trading and climate finance, forests emerge as valuable assets.

Forest-based solutions, such as afforestation and reforestation projects, enable businesses to offset their carbon footprints.
Participating in carbon markets and climate finance initiatives can provide a new revenue stream for landowners and communities involved in sustainable forest management.
Moreover, corporations are increasingly recognizing the importance of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR).
Investing in forest-based solutions allows businesses to demonstrate a commitment to sustainability and environmental conservation, enhancing their public image and potentially attracting environmentally conscious consumers.
the profitability of forest-based solutions in providing ecosystem services is a compelling narrative for businesses and communities alike.
Beyond the intrinsic value of preserving biodiversity and mitigating climate change, these solutions offer tangible economic benefits.
By embracing sustainable practices and recognizing the economic potential of intact ecosystems.
Stakeholders can create a win-win scenario where profitability and environmental stewardship go hand in hand.

CONCLUSION
In the tapestry of time, where the fate of humanity and the health of our planet are intricately woven together.
The exploration of forest-based solutions for sustainable agriculture emerges not just as a narrative but as a manifesto—a clarion call for a paradigm shift that transcends the boundaries of conventional thinking.
The profound journey through the myriad ways in which forests offer a lifeline to both our ecosystems and societies has unfolded as a powerful testimony to the urgent need for transformative action.
At the core of our exploration lies a fundamental truth: forests are not mere resources to be exploited but living, breathing entities that cradle the intricate balance of life on Earth.
The concept of agroforestry transcends the ordinary, beckoning us to reimagine agriculture not as an isolated endeavor but as a harmonious coexistence between human cultivation and the natural world.
It is a call to arms for a sustainable, resilient agricultural future—one that recognizes the interconnectedness of all living beings.
The economic tapestry woven by forest-based solutions is vibrant and rich, echoing the symphony of sustainability.
In the careful cultivation of non-timber forest products (NTFPs), we discover a sustainable economic model that treasures biodiversity as a source of wealth.

Communities, once tethered to the extractive model of timber harvesting, now find prosperity in the diverse array of products the forest graciously provides.
It is an economic awakening—a realization that in the preservation of biodiversity lies the key to enduring prosperity.
The harmonious dance between trees and crops in agroecosystems is a revelation, an intricate ballet that underscores the importance of holistic land management.
This dance is not just about agricultural productivity; it’s a celebration of soil health, nutrient cycling, and microclimatic regulation—a choreography that ensures the land remains fecund for generations to come.
The marriage of agriculture and forests is not one of convenience but one of necessity—an alliance that safeguards the very foundation of our sustenance.
The economic ripples extend far beyond local communities through the promise of ecotourism.
Forests, once seen as remote and untouched, become both a destination and a source of livelihood.
This economic transformation is not a mere byproduct but a deliberate choice, where the preservation of pristine landscapes becomes a commodity in itself.
The economic value of intact ecosystems is rediscovered, creating a model where tourism is not a threat but a partner in the conservation narrative.
As we venture into the uncharted territories of carbon markets and climate finance, we unearth a groundbreaking reality—forests as assets in the global fight against climate change.
The carbon sequestration prowess of trees becomes not just an environmental virtue but a tradable commodity.
The concept of carbon trading positions forests as allies in a global effort to mitigate climate change—a role that transcends regional boundaries and national interests.
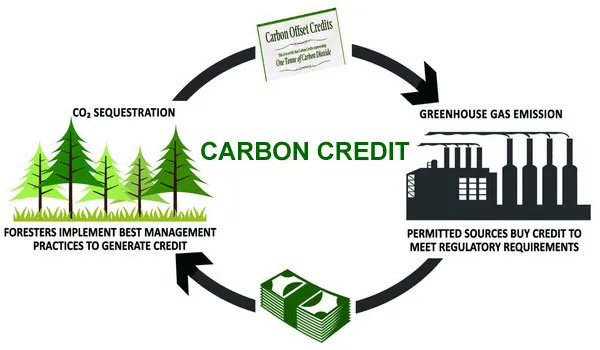
It is a realization that the health of our planet is a collective responsibility, and forests are instrumental players in this grand symphony of climate resilience.
In the corporate boardrooms of the world, the adoption of forest-based solutions becomes a cornerstone of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR).
It is a shift from a profit-centric mindset to one that recognizes the intrinsic value of investing in the preservation of ecosystems.
This strategic shift is not merely a nod to ethical considerations but a realization that sustainable business practices are not antithetical to economic success;
Rather, they are the bedrock upon which long-term, resilient economies are built.
As we reflect on the journey through the realms of sustainable agriculture and forest-based solutions.
The conclusion becomes not just an endpoint but a crossroads—a juncture where the choices we make resonate through time.
The unlocking of ecosystem services through forest-based solutions is a declaration that our path forward is not a binary choice between progress and preservation.
It is a nuanced journey where the two are inextricably linked—a journey towards a future where prosperity is not a fleeting moment but a sustained, regenerative force.
In the symphony of sustainability, let the melody of the forests guide us towards a future where prosperity is measured not just in economic terms but in the vitality of our planet and the well-being of all its inhabitants.
As we inscribe the final notes in this manifesto for change, let it echo through the corridors of policy, resonate in the decisions of businesses, and reverberate in the hearts of individuals.
For in the tapestry of time, the story of forest-based solutions and sustainable agriculture is not just a chapter;
it is the anthem of hope, resilience, and a harmonious coexistence with the Earth.





Leave a Reply