Wind Energy: 5 Economic Opportunities in Offshore Wind Farms
Wind energy has emerged as a pivotal player in the global transition towards sustainable and renewable power sources.
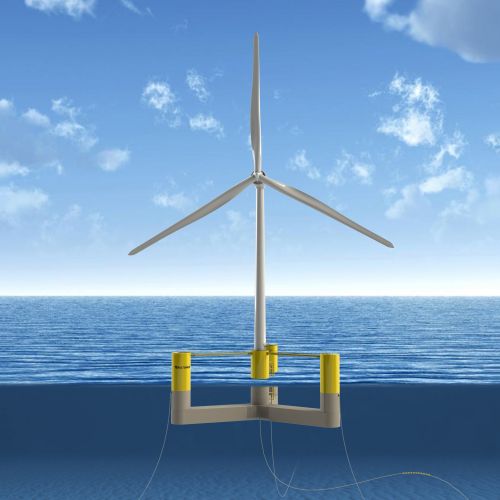
In this context, offshore wind farms present a compelling frontier, offering a myriad of opportunities along with unique challenges.
As the world grapples with the imperative to reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change, the prospects of harnessing wind energy at sea have garnered increasing attention.
One of the primary opportunities in offshore wind farms lies in their vast potential for power generation.
Coastal areas and expanses of open sea offer strong and consistent wind patterns, enabling more efficient and reliable energy production compared to onshore counterparts.
This reliability translates into a higher capacity factor, ensuring a more stable and constant electricity supply to meet the growing global energy demand.
Moreover, offshore wind farms contribute to diversifying the renewable energy portfolio.
By tapping into the power of ocean winds, countries can reduce their dependence on fossil fuels and enhance energy security.
The decentralized nature of offshore wind farms also allows for energy production closer to densely populated coastal regions.
Minimizing transmission losses and improving overall grid resilience.
However, these opportunities come hand in hand with a set of distinct challenges.
The logistical and engineering complexities of constructing and maintaining structures in the harsh marine environment pose significant hurdles.
Offshore wind farms require specialized technology and expertise, leading to higher initial investment costs compared to onshore projects.
Overcoming these challenges necessitates advancements in offshore engineering, materials science, and logistics to make offshore wind economically competitive.
Another critical challenge is posed by environmental considerations. Offshore wind farms can impact marine ecosystems and bird migration patterns.
Striking a balance between renewable energy generation and environmental conservation requires careful planning, environmental impact assessments, and the implementation of mitigation measures.
Collaboration between the wind energy industry, environmental organizations, and regulatory bodies is essential to ensure the sustainable development of offshore wind projects.
The opportunities presented by offshore wind farms are immense, contributing to the global shift towards cleaner and more sustainable energy sources.
However, addressing the associated challenges requires innovation, collaboration, and a commitment to environmental stewardship.
As technology advances and best practices evolve, offshore wind energy stands poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of the global energy landscape.
5 Economic Opportunities in Offshore Wind Farms
The burgeoning field of offshore wind energy not only holds promise for addressing environmental concerns but also presents a host of economic opportunities.
Here, we delve into five key economic aspects that underscore the potential for economic growth and development within the realm of offshore wind farms.
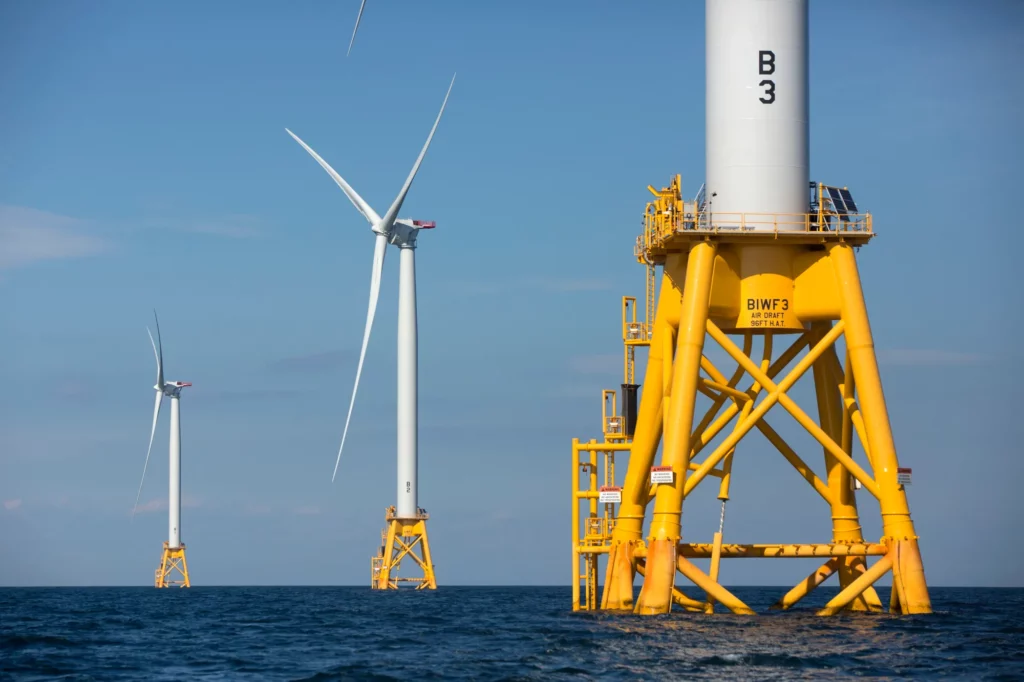

- Job Creation: One of the most immediate economic benefits of offshore wind farms is the creation of jobs. The development, construction, and maintenance of these facilities necessitate a skilled workforce, ranging from engineers and project managers to technicians and support staff. This job creation contributes to local and regional economies, fostering employment opportunities and skill development in communities near offshore wind projects.
- Supply Chain Growth: The establishment of offshore wind farms stimulates the growth of a robust supply chain, fostering economic activity across various industries. Manufacturers of wind turbines, cables, and other components find new markets, while service providers catering to logistics, vessel operations, and maintenance services witness increased demand. This ripple effect extends to small and medium-sized enterprises, contributing to a diversified and resilient economy.
- Investment and Financing Opportunities: Offshore wind projects require substantial upfront investment, presenting opportunities for investors and financial institutions. As governments and private entities seek to expand their renewable energy portfolios, financing options, including green bonds and project financing, become attractive avenues. This influx of capital not only supports individual projects but also bolsters the broader financial ecosystem surrounding renewable energy.
- Technology and Innovation Advancements: The pursuit of offshore wind energy encourages technological innovation and research and development. Companies engaged in developing cutting-edge solutions for offshore wind face a competitive landscape that fosters advancements in turbine design, installation techniques, and maintenance technologies. This innovation not only improves the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of offshore wind projects but also positions countries and companies as leaders in the renewable energy sector.
- Export and Trade Opportunities: Countries with well-established offshore wind industries can tap into export opportunities, leveraging their expertise to provide technology, knowledge, and services to regions seeking to develop their own offshore wind capabilities. This not only enhances diplomatic and economic ties but also contributes to a global transition toward sustainable energy practices. Exporting expertise and technology related to offshore wind can become a significant driver of economic growth and international collaboration.
The economic opportunities within offshore wind energy extend far beyond the immediate generation of electricity.
By fostering job creation, supporting a diverse supply chain, attracting investments, driving technological innovation, and facilitating international trade, offshore wind farms play a pivotal role in shaping a sustainable and economically vibrant future.
As nations continue to invest in renewable energy, the economic benefits of offshore wind are poised to make a lasting impact on both local and global scales.
ORGANISATIONS/NGOs PROMOTING ECONOMIC OPPORTUNITIES IN OFFSHORE WIND FARMS
Various organizations and non-governmental organizations (NGOs) play pivotal roles in facilitating economic opportunities within the offshore wind energy sector.
Their efforts range from policy advocacy and research to project development and community engagement, contributing to the growth and sustainability of offshore wind farms.
- International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA): IRENA is a global intergovernmental organization that focuses on promoting renewable energy. It plays a crucial role in facilitating collaboration among countries, sharing best practices, and providing policy guidance. IRENA’s support can foster a conducive global environment for offshore wind development, attracting investments and promoting economic opportunities.
- WindEurope: As the voice of the wind industry in Europe, WindEurope brings together industry stakeholders, including companies, research institutions, and NGOs. This organization actively engages in policy advocacy, market intelligence, and promoting the economic benefits of wind energy, including offshore wind. WindEurope’s initiatives contribute to creating a favorable business environment and economic opportunities for stakeholders.
- Global Wind Energy Council (GWEC): GWEC is a global organization that works towards the expansion of wind energy worldwide. It plays a vital role in advocating for policies that support wind energy deployment and provides a platform for industry collaboration. Through its initiatives, GWEC can influence the economic landscape of offshore wind by encouraging investment and fostering cross-border cooperation.
- Environmental NGOs (e.g., Greenpeace, World Wildlife Fund – WWF): Environmental NGOs are increasingly involved in the renewable energy transition, including offshore wind. These organizations often collaborate with industry players and governments to ensure sustainable and environmentally responsible practices. Their involvement helps shape policies that balance economic opportunities with ecological considerations, ensuring the long-term viability of offshore wind projects.
- The Business Network for Offshore Wind: Operating in the United States, this business-focused organization aims to accelerate the development of the offshore wind industry. By connecting businesses, promoting supply chain growth, and advocating for policies that support the sector, the Business Network for Offshore Wind contributes to the economic opportunities within the U.S. offshore wind industry.
- National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL): In the United States, NREL plays a critical role in advancing renewable energy technologies. It conducts research and provides technical expertise to support the development and deployment of offshore wind projects. NREL’s work contributes to reducing costs, improving efficiency, and enhancing the economic viability of offshore wind energy.
- Offshore Wind California: This organization focuses specifically on advancing offshore wind development in California, promoting economic opportunities for businesses and communities. By engaging with stakeholders, advocating for policies, and supporting project development, Offshore Wind California contributes to the growth of the offshore wind industry on the U.S. West Coast.

Collaboration among these organizations and NGOs is essential for creating a supportive ecosystem for offshore wind energy.
Through research, advocacy, and project facilitation, they contribute to the realization of economic opportunities, job creation, and sustainable development within the offshore wind sector.
As the industry continues to expand globally, the role of these organizations becomes increasingly crucial in ensuring a responsible and economically vibrant offshore wind energy landscape.
HOW TO FIND ORGANISATIONS/NGOs PROMOTING ECONOMIC OPPORTUNITIES IN OFFSHORE WIND FARMS
Finding organizations and non-governmental organizations (NGOs) that are actively engaged in promoting economic opportunities in offshore wind farms requires a targeted approach.
Here are some strategies and resources to identify these entities:
- Government Agencies and Energy Departments: Start by exploring the websites of government agencies and energy departments at national and regional levels. These entities often collaborate with organizations and NGOs to advance renewable energy goals. For example, in the United States, the Department of Energy (DOE) and the Bureau of Ocean Energy Management (BOEM) provide information and links to stakeholders involved in offshore wind development.
- International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA): IRENA is a key international organization that promotes renewable energy globally. Its website offers resources, reports, and information on various aspects of renewable energy, including offshore wind. By exploring IRENA’s publications and initiatives, you can identify organizations and NGOs involved in economic opportunities within offshore wind energy.
- Industry Associations: Check industry associations related to renewable energy and offshore wind. Associations like WindEurope, the Global Wind Energy Council (GWEC), and the American Wind Energy Association (AWEA) often collaborate with organizations and NGOs. Their websites provide insights into the industry landscape, events, and members, including those focused on economic aspects.
- Online Directories and Platforms: Utilize online directories and platforms dedicated to renewable energy and sustainability. Platforms like Clean Energy Directory, Renewable Energy World, and OffshoreWind.biz provide comprehensive lists of companies, organizations, and NGOs involved in offshore wind projects and related economic activities.
- Research Institutions and Think Tanks: Explore the websites of research institutions and think tanks specializing in energy and environmental studies. These organizations often collaborate with industry players and contribute valuable research. Institutions like the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), Fraunhofer Institute, and the Energy Research Centre of the Netherlands (ECN) can provide insights into economic opportunities in offshore wind.
- Networking at Industry Events: Attend conferences, seminars, and industry events focused on renewable energy and offshore wind. These gatherings provide opportunities to network with professionals, representatives from NGOs, and officials from relevant organizations. Industry events often host panel discussions and exhibitions where you can connect with stakeholders.
- Local Chambers of Commerce and Business Networks: Explore local chambers of commerce and business networks in regions with active offshore wind development. These organizations often have information on businesses, NGOs, and associations involved in the industry. Chambers of commerce in coastal areas or regions with offshore wind projects can be particularly valuable.
- Social Media and Online Communities: Engage with social media platforms and online communities dedicated to renewable energy and offshore wind. Platforms like LinkedIn and industry-specific forums provide a space for professionals and organizations to share updates, discuss trends, and connect with potential partners.

By combining these strategies, you can build a comprehensive list of organizations and NGOs involved in promoting economic opportunities in offshore wind farms.
It’s important to stay updated on industry developments and actively participate in relevant networks to foster connections and collaborations within the offshore wind energy sector.
CONCLUSION:
In conclusion, the journey through the realm of offshore wind energy reveals a landscape rich with both promise and complexity.
The opportunities embedded within the undulating currents of the open sea offer a tantalizing vision of a future where sustainable power generation becomes not just an aspiration but a dynamic reality.
The challenges, though formidable, are the crucible in which innovation, resilience, and environmental stewardship must converge to shape a trajectory toward a cleaner and more sustainable energy future.
The economic opportunities within offshore wind farms, as we have explored, extend far beyond the immediate horizon of energy production.
Job creation, supply chain growth, investment avenues, technological innovation, and the facilitation of international trade all stand as pillars supporting a vibrant and resilient economic ecosystem.
These opportunities are not only a testament to the potential of offshore wind as an energy source but also a beacon illuminating the path toward economic prosperity and energy security on a global scale.
Yet, as we bask in the promise of economic growth and environmental stewardship, the challenges demand our unwavering attention and collaborative resolve.
The harsh marine environment, logistical intricacies, and environmental considerations necessitate a harmonious dance between technological advancements, regulatory frameworks, and ecological sensitivity.
Striking this delicate balance is not just a prerequisite for sustainable offshore wind development but a moral imperative as we chart a course toward a future where energy demands harmonize with environmental preservation.
As offshore wind energy asserts its significance on the world stage, the role of governments, industry players, environmental advocates, and communities becomes increasingly pivotal.
Policies that foster innovation, international collaboration that transcends geopolitical boundaries.

And community engagement that ensures the benefits are shared equitably – these are the ingredients that will fortify the foundation upon which the offshore wind industry stands.
In this grand tapestry of possibilities and challenges, offshore wind farms emerge not merely as structures dotting the seascape but as symbols of human ingenuity and determination.
They embody our collective pursuit of a sustainable future, where the ceaseless dance of the wind across the oceans becomes a choreography of progress, resilience, and responsible coexistence with our planet.
The opportunities are vast, the challenges are daunting, but within this crucible lies the transformative power to reshape our energy landscape and, by extension, the destiny of generations yet unborn.
The winds of change are blowing, beckoning us to navigate these uncharted waters with courage, wisdom, and a steadfast commitment to the promise of a cleaner, brighter tomorrow.





Leave a Reply