Smart Grid Technology: Navigating the Future and Unraveling the Potentials
Introduction:
In the dynamic landscape of the 21st century, the demand for sustainable and efficient energy solutions has driven the evolution of conventional power grids into sophisticated networks known as Smart Grids.
Smart Grid Technology represents a revolutionary paradigm shift in the way we generate, distribute, and consume electrical energy.
By seamlessly integrating advanced communication, sensing, and control technologies.
These intelligent grids hold the promise of enhancing grid reliability, optimizing energy consumption, and accommodating the growing influx of renewable energy sources.
This article delves into the core concepts of Smart Grid Technology, unraveling its intricacies and exploring the transformative potential it holds for the future of energy.
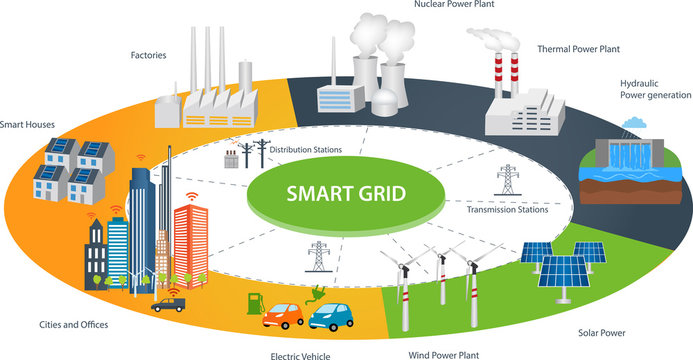
Understanding Smart Grid Technology: At its essence, Smart Grid Technology is an intricate web of interconnected devices and systems that leverage cutting-edge digital communication and real-time data analytics to optimize the generation, distribution, and consumption of electricity. Unlike traditional power grids.

Smart Grids enable bidirectional communication between utilities and consumers, fostering a more responsive and adaptable energy ecosystem.
The backbone of Smart Grids lies in their ability to intelligently monitor and manage electrical flow, allowing for real-time adjustments based on demand fluctuations.
Advanced sensors, smart meters, and automation technologies empower utilities to proactively identify and address potential issues, minimizing downtime and enhancing overall grid resilience.
This level of responsiveness is a key feature, especially in an era where the global energy landscape is undergoing a transformative shift towards decentralized and renewable energy sources.
Key Components of Smart Grids:
- Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI): Smart Grids deploy sophisticated metering systems that provide granular insights into energy consumption patterns. This two-way communication allows for dynamic pricing models, encouraging consumers to optimize their energy usage during peak and off-peak hours.
- Distribution Automation: Smart Grids utilize automation technologies to remotely monitor, control, and optimize the distribution of electricity. This ensures efficient energy delivery, minimizes losses, and enhances the overall reliability of the grid.
- Renewable Energy Integration: With an increasing emphasis on sustainability, Smart Grids seamlessly integrate renewable energy sources like solar and wind into the grid. Intelligent management of these intermittent sources helps maintain grid stability while reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- Grid Storage Systems: To address the intermittent nature of renewable energy, Smart Grids incorporate energy storage solutions. This enables the efficient storage and release of excess energy, ensuring a steady and reliable power supply even when renewable sources are not actively generating electricity.

In the subsequent sections, we will delve deeper into these components, exploring how each contributes to the transformative potential of Smart Grid Technology and its impact on the way we produce and consume energy in the modern era.
The Evolution of Energy Management: Smart Grid Technology is, in many ways, a response to the changing dynamics of energy consumption.
As traditional power grids struggle to cope with the demands of a rapidly growing population and the increasing integration of renewable energy sources
The need for a more adaptive and intelligent energy management system becomes imperative.
One of the defining features of Smart Grids is their ability to facilitate Demand Response programs.
By leveraging real-time data and communication capabilities, utilities can engage consumers in actively adjusting their energy usage during peak times.
This not only helps prevent grid overloads but also empowers consumers with the knowledge and tools to make informed decisions about their energy consumption, fostering a culture of energy efficiency.
Enhancing Grid Resilience and Reliability: The inherent intelligence embedded within Smart Grids significantly enhances the resilience and reliability of the overall energy infrastructure.
Rapid detection and response to faults or outages, often before consumers even notice, minimize downtime and contribute to a more robust energy delivery system.
Automated rerouting of power, self-healing capabilities, and the ability to isolate and contain issues ensure that disruptions are localized, preventing widespread blackouts.
Moreover, the integration of sensors and monitoring devices at various points within the grid enables predictive maintenance.
By identifying potential equipment failures before they occur, utilities can schedule proactive maintenance.
Reducing the likelihood of unexpected breakdowns and extending the lifespan of critical infrastructure.
Empowering Consumers and Enhancing Efficiency: Smart Grid Technology places a considerable emphasis on empowering end-users with information and control over their energy consumption.
Advanced metering systems provide consumers with real-time insights into their energy usage patterns.
Allowing them to make informed decisions about when and how they use electricity.
This not only facilitates cost savings but also encourages a more conscious and sustainable approach to energy consumption.
Additionally, the integration of electric vehicle charging infrastructure into Smart Grids supports the growing trend of electric mobility.
Smart Charging systems can optimize the charging process, considering factors such as grid demand, renewable energy availability, and cost.
Contributing to the seamless integration of electric vehicles into the broader energy ecosystem.
As we navigate the future of energy, Smart Grid Technology emerges as a beacon of innovation and efficiency.
Its transformative capabilities extend beyond the traditional boundaries of power grids, offering a holistic approach to sustainable energy management.
From enhancing grid resilience to empowering consumers and seamlessly integrating renewable sources.
Smart Grids represent a pivotal step towards a more intelligent, adaptive, and sustainable energy future.
In the subsequent sections of this exploration, we will delve deeper into the specific components and applications of Smart Grid Technology.
Unlocking the full spectrum of possibilities within this dynamic field.
The Advent of Smart Grid: Transforming Energy Management in the 21st Century
The advent of Smart Grid marks a pivotal moment in the evolution of energy management.

Heralding a departure from traditional grid systems towards a more intelligent, responsive, and sustainable paradigm.
The roots of Smart Grid can be traced back to the early 21st century when the global energy landscape faced unprecedented challenges.
Prompting a reevaluation of how we generate, distribute, and consume electricity.
Challenges Igniting Transformation: The turn of the century witnessed a confluence of factors that spurred the need for a transformative approach to energy management.
Rapid urbanization, population growth, and the escalating demand for electricity placed unprecedented stress on aging power infrastructures.
Simultaneously, the increasing integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, introduced complexities related to their intermittency and decentralized generation.
Traditional grids, designed for a one-way flow of electricity from centralized power plants to consumers, struggled to adapt to these dynamic challenges.
Instances of grid failures, rising energy costs, and the urgent call for reducing carbon footprints fueled a collective recognition that a fundamental shift was necessary to address the intricacies of the modern energy landscape.
The Birth of Smart Grid Concept: The concept of Smart Grid emerged as a response to the limitations of conventional grids.

It envisioned an energy ecosystem infused with digital intelligence, real-time communication, and advanced control mechanisms.
Smart Grids aimed not only to modernize the existing infrastructure but also to create a flexible,
Adaptive system capable of accommodating the diverse sources and patterns of energy production and consumption.
Key to the Smart Grid concept was the integration of cutting-edge technologies, including sensors, communication networks, and data analytics.
This amalgamation would enable utilities to monitor the grid in real-time, anticipate challenges, and respond dynamically to fluctuations in demand and supply.
The two-way communication between utilities and end-users became a linchpin for facilitating more informed and efficient energy consumption.
Core Components of Smart Grid: Smart Grids comprise a set of interconnected components that work synergistically to revolutionize energy management.
Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI), distribution automation, grid storage systems, and the incorporation of renewable energy sources became integral elements.
These components collectively aimed to enhance grid reliability, optimize energy distribution, and foster a more sustainable energy ecosystem.
Benefits Unveiled: The advantages promised by Smart Grid Technology were multifaceted. Improved grid reliability and resilience, reduced energy losses, increased energy efficiency.
And the seamless integration of renewable energy sources were among the many benefits touted.
Additionally, the empowerment of consumers through real-time data and the facilitation of demand response programs promised to create a more engaged and energy-conscious society.
Current Landscape and Future Trajectory: As Smart Grids continue to be deployed and refined, their impact on the global energy landscape becomes increasingly evident.
Many regions have embraced pilot projects and large-scale implementations, showcasing the tangible benefits of this transformative technology.
The ongoing research and development in areas such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), and grid cybersecurity indicate a commitment to refining and expanding the capabilities of Smart Grids in the years to come.
The advent of Smart Grid marks a paradigm shift in how we conceive, manage, and utilize electrical energy.
From addressing immediate challenges to fostering a sustainable energy future, Smart Grid Technology stands as a testament to human ingenuity and the relentless pursuit of a more efficient, resilient, and environmentally conscious energy ecosystem.
As this journey unfolds, the transformative potential of Smart Grids continues to shape the future of energy worldwide.
Exploring Investment Opportunities in Smart Grid Technology: Powering the Future of Energy
Investing in Smart Grid technology presents a compelling opportunity for individuals and institutions looking to align their portfolios with the transformative trends shaping the energy sector.
As the world increasingly shifts towards sustainable and efficient energy solutions, Smart Grids emerge as a critical enabler, offering diverse investment avenues across various sectors.
Here’s a closer look at the investment opportunities available in Smart Grid technology:

1. Infrastructure Development: Investors can participate in the deployment and expansion of Smart Grid infrastructure.
This includes financing the development of advanced metering systems, distribution automation, and grid storage solutions.
Infrastructure investments are crucial for supporting the widespread adoption of Smart Grid technology, particularly in regions aiming to modernize their electrical grids.
2. Technology Providers: Companies at the forefront of developing Smart Grid technologies represent a lucrative investment opportunity.
This category includes businesses engaged in the manufacturing of smart meters, sensors, communication devices, and grid management software.
Investing in technology providers allows investors to capitalize on the growing demand for innovative solutions driving the Smart Grid revolution.
3. Renewable Energy Integration: As Smart Grids seamlessly integrate renewable energy sources into the electrical grid, there are investment opportunities in companies involved in renewable energy production.
This encompasses solar and wind energy companies, as well as those specializing in energy storage solutions to address the intermittent nature of renewable sources.
4. Data Analytics and IoT: The success of Smart Grids heavily relies on advanced data analytics and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies.
Investors can explore opportunities in companies developing analytics platforms, machine learning algorithms, and IoT devices tailored for the energy sector.
These technologies enable utilities to make data-driven decisions, optimize energy distribution, and enhance overall grid efficiency.
5. Cybersecurity Solutions: With the increased digitization of the energy sector, there is a growing need for robust cybersecurity solutions to protect Smart Grids from potential cyber threats.
Investors can consider cybersecurity firms specializing in safeguarding critical infrastructure, including those focused on securing the communication networks and data centers integral to Smart Grid operations.
6. Demand Response Platforms: Investing in companies that offer demand response platforms provides exposure to the evolving landscape of consumer engagement within Smart Grids.
These platforms enable end-users to actively manage and optimize their energy consumption, contributing to grid stability and efficiency.
Companies in this space can offer innovative solutions for both utilities and consumers.

7. Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Infrastructure: The integration of electric vehicles into Smart Grids creates opportunities for investments in EV charging infrastructure.
Companies involved in the development and deployment of smart charging stations, grid-to-vehicle technologies, and related services stand to benefit from the intersection of Smart Grids and the growing electric mobility trend.
8. Utility Companies Embracing Smart Grids: Investors can explore opportunities within utility companies that are actively investing in and deploying Smart Grid technologies.
These companies are well-positioned to enhance grid reliability, reduce operational costs, and meet regulatory requirements.
Investing in forward-thinking utilities aligns with the broader trend of grid modernization.
Smart Grid technology presents a multifaceted investment landscape, spanning infrastructure development.
Technological innovation, renewable energy integration, and consumer-centric solutions.
As the global energy sector continues its transition towards sustainability and efficiency, strategically positioned investments in Smart Grid technology offer the potential for long-term growth and positive environmental impact.
However, like any investment, careful due diligence is essential to navigate the dynamic and evolving nature of the Smart Grid market.
5 Major Countries and Companies Investing in Smart Grid
1. United States: The United States has been a trailblazer in the deployment of Smart Grid technology, with significant investments from both public and private entities.
The Department of Energy’s (DOE) Smart Grid Investment Grant (SGIG) program, launched in 2009, allocated substantial funds to modernize the country’s electrical infrastructure.
Major utility companies like PG&E, Southern Company, and Duke Energy have spearheaded Smart Grid initiatives, investing in advanced metering systems, distribution automation, and grid modernization projects.
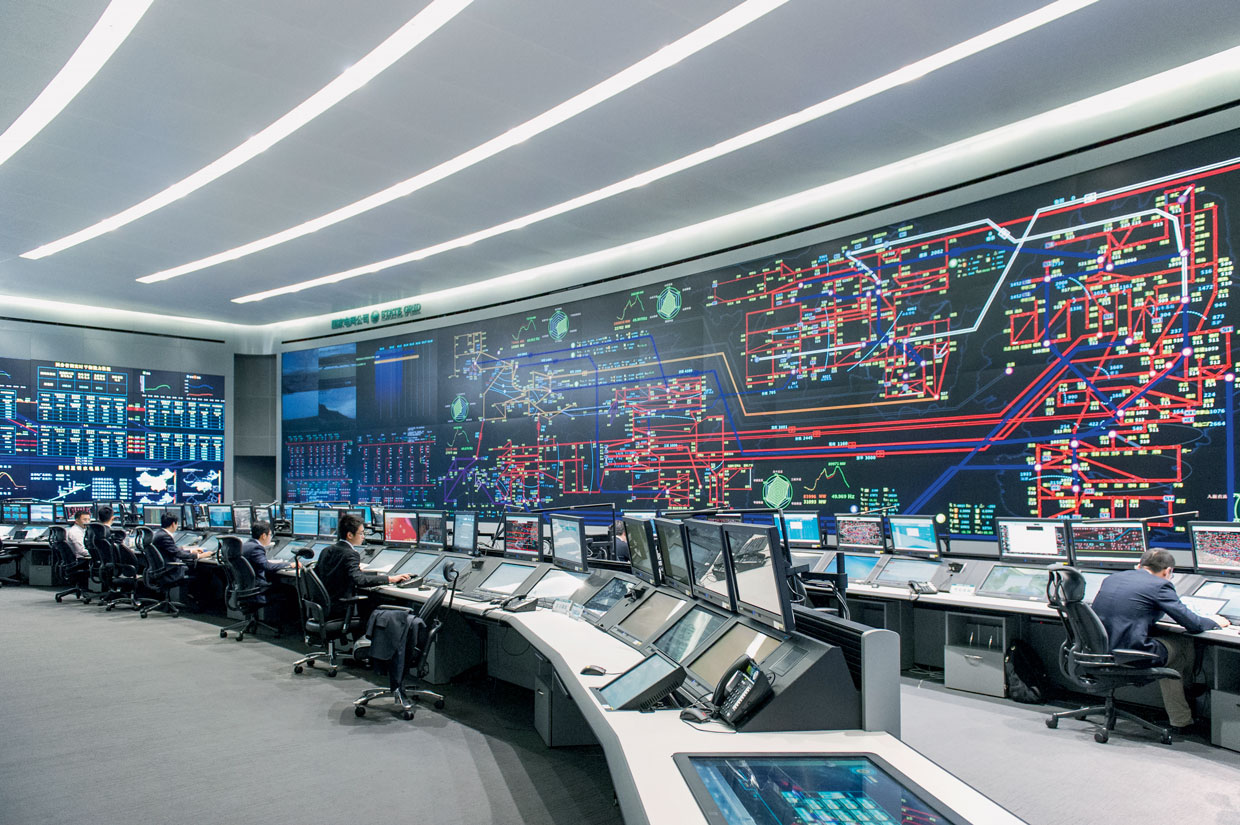
2. China: China, as a global leader in technology adoption and renewable energy, has been actively investing in Smart Grid initiatives.

State Grid Corporation of China (SGCC), the world’s largest utility company, has played a pivotal role in deploying Smart Grid technologies across the country.
China’s focus on integrating renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar, into the grid has led to substantial investments in Smart Grid infrastructure for efficient energy management and distribution.
3. Germany: Germany, known for its commitment to renewable energy and sustainability, has invested significantly in Smart Grid technology.
The country’s transition to a decentralized energy system, known as the “Energiewende,” involves integrating a substantial share of renewable energy into the grid.
Companies like Siemens and Deutsche Telekom have been actively involved in providing Smart Grid solutions, supporting the transformation of the energy landscape in Germany.
4. Japan: Japan, with its technological innovation and commitment to energy efficiency, has made notable investments in Smart Grid initiatives.
The country’s focus on enhancing grid reliability and integrating renewable energy aligns with its broader goals of reducing carbon emissions.
Companies like Toshiba and Hitachi have been involved in developing advanced technologies for Smart Grid applications.
Contributing to Japan’s efforts to create a more resilient and sustainable energy infrastructure.

5. South Korea: South Korea has emerged as a key player in Smart Grid technology adoption, driven by a strong emphasis on technology innovation and energy efficiency.
Korea Electric Power Corporation (KEPCO), the country’s major utility company, has been at the forefront of Smart Grid deployment.
South Korea’s investments include projects related to advanced metering infrastructure, demand response systems, and the integration of smart technologies for grid optimization.

These countries, along with notable companies within their borders, have demonstrated a commitment to Smart Grid technology.
Recognizing its potential to enhance energy efficiency, promote sustainability, and address the challenges of modernizing electrical grids.
The investments made by these countries and companies underscore the global importance of Smart Grids in shaping the future of energy management and distribution.
As Smart Grid technology continues to evolve, collaboration and investment from key players around the world will play a crucial role in advancing its widespread adoption.
CONCLUSIONS
Powering Tomorrow through Smart Grid Technology
In the labyrinth of modern energy challenges, Smart Grid technology emerges as the guiding light, illuminating a path towards a future where sustainability, efficiency, and resilience converge.
As we traverse the dynamic landscape of global energy, the strategic investments and pioneering initiatives in Smart Grids by countries and corporations stand as beacons of progress.
Shaping a narrative of innovation, adaptability, and environmental stewardship.
The United States, a vanguard of technological innovation, has exemplified a commitment to grid modernization through robust Smart Grid investments. Utility giants such as PG&E, Southern Company, and Duke Energy have not merely embraced Smart Grids as a technological upgrade but as a transformative force reshaping the very foundations of the energy ecosystem. The United States, with its forward-thinking approach, lays the groundwork for a paradigm shift in the way nations manage and distribute electricity.
In the East, China’s monumental strides in Smart Grid technology echo its overarching ambition to lead the world in sustainable energy practices. The State Grid Corporation of China (SGCC), a titan in the utility realm, orchestrates a symphony of innovation, weaving Smart Grid technologies seamlessly into the fabric of the nation’s energy infrastructure. As China fortifies its grid against the challenges of the 21st century, it becomes a testament to the global impact of Smart Grids in balancing economic growth with environmental responsibility.

Germany: a crucible of renewable energy transition, amplifies the harmonious integration of Smart Grids within its Energiewende framework. Siemens and Deutsche Telekom, among others, sculpt a narrative of precision and sustainability, crafting Smart Grid solutions that resonate with the country’s commitment to a decentralized and eco-friendly energy future. In Germany, the Smart Grid is not merely a technological evolution but a manifestation of a societal ethos aligning progress with ecological balance.
Japan: The Land of the Rising Sun, Japan, integrates its technological prowess with a resilient spirit to champion Smart Grid initiatives.
Toshiba and Hitachi, among other innovators, engineer Smart Grid technologies that not only fortify the nation against energy vulnerabilities but also harmonize seamlessly with its cultural values of balance and foresight.
Japan’s Smart Grid investments unfold as a testament to the convergence of technological advancement and cultural ethos in building a sustainable energy legacy.
South Korea: propelled by a dynamic tech-driven landscape, has etched its presence in the Smart Grid narrative through the pioneering efforts of Korea Electric Power Corporation (KEPCO).
As South Korea ambitiously charts a course towards energy efficiency, KEPCO orchestrates a symphony of Smart Grid technologies.
Embodying the nation’s dedication to progress rooted in technological sophistication.
In South Korea, the Smart Grid becomes an embodiment of national aspirations, blending technology with a vision for a more sustainable and resilient future.
The trajectory of Smart Grid technology transcends geographical boundaries, weaving a global narrative of collaboration, innovation, and collective responsibility.
The investments made by these major players underscore a shared commitment to a future where energy is not just a resource but a conscientious, dynamic ecosystem.

As Smart Grids become the cornerstone of tomorrow’s energy architecture, the synergy of countries and corporations investing in this transformative technology heralds a future where power isn’t just harnessed;
It’s intelligently orchestrated, empowering nations and communities to thrive in an era where energy isn’t just consumed but coexisted with, harmonizing progress with planetary health.
The story of Smart Grids is not just about technological evolution; it’s about the power to shape a future where energy is not just a commodity but a catalyst for a better world.





Leave a Reply