Harnessing Earth’s Heat: Unveiling The Geothermal Energy With 7 Countries and Companies Leading the Charge
Unlocking Sustainable Power from the Earth’s Core
In the quest for sustainable and eco-friendly energy sources, the geothermal energy has emerged as a promising solution.
Harnessing the Earth’s heat for power generation not only provides a continuous and reliable source of electricity.
But also significantly reduces the carbon footprint associated with traditional energy methods.
This comprehensive article explores the concept of geothermal energy, its benefits, challenges, and the technology driving this transformative energy sector.
Understanding Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy is derived from the heat stored within the Earth’s core.
The planet’s mantle, composed of molten rock and metals, produces a continuous flow of thermal energy.
This heat can be tapped into through various methods to generate electricity or directly provide heating for residential and industrial purposes.
Advantages of the Geothermal Energy
- Renewable and Sustainable: Geothermal energy is a virtually limitless resource, as the Earth’s heat is continually produced.
- Low Environmental Impact: Compared to fossil fuels, geothermal energy production emits minimal greenhouse gases, contributing to cleaner air and mitigating climate change.
- Stable and Reliable: Unlike solar and wind energy, geothermal power generation is not dependent on weather conditions, providing a stable and reliable source of electricity.
Challenges and Solutions
- Location Dependency: Geothermal resources are more abundant in certain regions, limiting global accessibility. However, advancements in technology are expanding the reach of geothermal energy projects.
- Initial Costs: The upfront costs of drilling and installing the geothermal power plants can be significant. Government incentives and technological innovations are addressing these economic barriers.
The Geothermal Technology in Action
- Binary Cycle Power Plants: These systems use the heat from the Earth to vaporize a working fluid, which then drives a turbine connected to a generator, producing electricity.
- Direct-Use Applications: Geothermal heat can be directly used for heating buildings, growing plants in greenhouses, or even for industrial processes.
Global Initiatives and Future Prospects
Countries worldwide are recognizing the potential of the geothermal energy and investing in research and development.
The global push towards renewable energy sources aligns with the increasing importance of geothermal power in the energy transition.
With ongoing advancements in technology and growing awareness of environmental sustainability, geothermal energy is poised to play a pivotal role in the future of clean energy.
Geothermal energy stands as a testament to human innovation, tapping into the Earth’s natural heat to provide a sustainable and reliable energy source.
As technology continues to evolve, and as the world seeks cleaner alternatives to traditional energy.
Geothermal power is set to become an integral component of our energy landscape, fostering a more sustainable and greener future.
Geothermal Energy: The Ingenious Process Unveiled
Geothermal energy harnesses the Earth’s internal heat through a process that involves extracting and converting thermal energy into electricity.
The key to this innovative method lies in the Earth’s mantle, where molten rock and metals continuously generate intense heat.
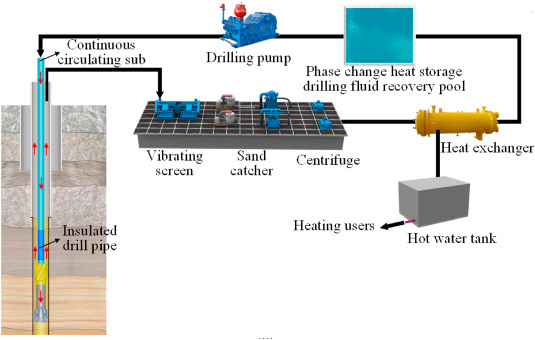
There are several ways in which this natural heat reservoir can be tapped into to produce power.
1. Heat Extraction through Drilling:
The most common method involves drilling deep into the Earth’s crust to access the hot rocks beneath.
These rocks, heated by the Earth’s mantle, release thermal energy that can be captured for power generation.
The deeper the well, the higher the temperatures encountered, resulting in more efficient energy extraction.
2. Binary Cycle Power Plants:
One prevalent technology in geothermal power generation is the use of binary cycle power plants.
In these systems, a heat-transfer fluid with a lower boiling point than water circulates in a closed-loop system.
As the hot geothermal fluid passes through a heat exchanger, it vaporizes the working fluid, typically an organic compound with a lower boiling point.
The vapor then drives a turbine connected to a generator, producing electricity.
The condensed fluid is then returned to the heat exchanger to repeat the cycle.
3. Direct Utilization of Geothermal Heat:
Beyond electricity generation, the geothermal energy has versatile direct-use applications. In areas where hot water or steam is readily accessible.
These resources can be channeled directly for heating purposes.
This method is especially popular in residential and industrial settings, providing a sustainable alternative to conventional heating systems.
4. Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS):
In regions with limited natural geothermal resources, Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS) come into play.
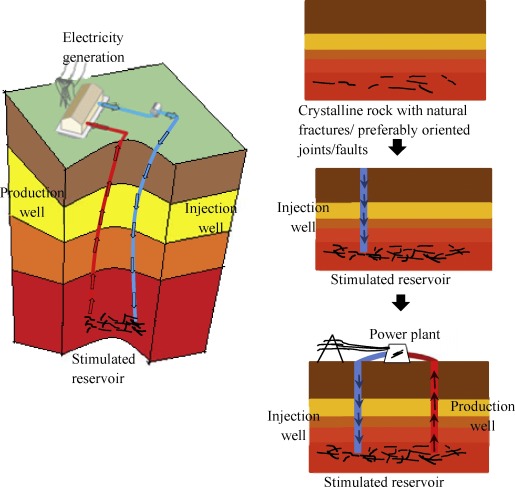
EGS involves artificially stimulating the extraction of heat from the Earth by creating fractures in hot rocks and then circulating water through the fractured zones to capture the released heat.
This method widens the geographical scope for the geothermal energy projects.
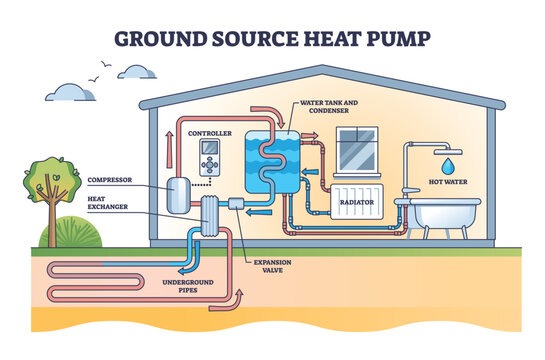
5. Geothermal Heat Pumps:
Geothermal heat pumps are another application, primarily used for heating and cooling buildings.
These systems leverage the relatively stable temperatures found just below the Earth’s surface to provide efficient heating in winter and cooling in summer.
In essence, geothermal energy works by tapping into the Earth’s internal heat reservoirs through various technologies.
Converting this thermal energy into electricity or utilizing it directly for practical applications.
As technological advancements continue to improve efficiency and expand the reach of geothermal projects, this renewable energy source is poised to become an increasingly integral part of our global energy landscape.
The Genesis of Geothermal Energy: A Historical Exploration
The discovery and utilization of the geothermal energy trace back to ancient times, with civilizations recognizing the Earth’s natural heat and harnessing it for various purposes.
The origins of geothermal energy can be attributed to both cultural practices and scientific curiosity.
1. Indigenous Knowledge and Ancient Practices:
Indigenous communities around the world, from the hot springs of ancient Rome to the geysers of Iceland, had long recognized the Earth’s internal heat.
These early societies utilized natural geothermal features for bathing, heating, and cooking.
The Romans, for instance, built elaborate bathhouses around hot springs, capitalizing on the warmth provided by the Earth.

2. Birth of Geothermal Science:
The scientific understanding of the geothermal energy began to evolve during the 19th century.
Sir William Herschel, a British astronomer, conducted experiments in the early 1800s that demonstrated the potential for harnessing heat from the ground.
He measured the temperature differences between shallow and deep holes, revealing that the Earth’s interior maintained a consistent warmth.
3. Pioneering Efforts in Italy:
Italy, a region known for its geothermal activity, played a pivotal role in the development of geothermal energy.
In the early 20th century, Prince Piero Ginori Conti conducted the world’s first successful attempt at generating electricity using geothermal steam in Larderello, Tuscany, in 1904.
This marked a significant milestone, showcasing the practical application of geothermal power.
4. The Birth of Geothermal Power Plants:
The first official geothermal power plant emerged in 1921 in the same region of Larderello, Italy.
The plant, designed by engineer Cesare Auguste Pisano, successfully generated electricity by utilizing steam from the Earth’s interior.
Following this success, other geothermal power plants were established in the region, solidifying geothermal energy’s place as a viable source of electricity.
5. Post-WWII Resurgence:
After World War II, the interest in geothermal energy experienced a resurgence.
Countries such as the United States and New Zealand began exploring and developing geothermal resources for electricity generation.
The first large-scale geothermal power plant in the United States,
The Geysers in California, began operation in the 1960s, marking a milestone in the global expansion of the geothermal energy.
Today, with a deeper understanding of the Earth’s subsurface and advancements in drilling technologies.
Geothermal energy has become an integral part of the renewable energy landscape.
The journey from ancient cultural practices to the modern utilization of geothermal power is a testament to humanity’s ability to harness and innovate with the natural resources provided by the Earth.
Global Geothermal Investments: Countries and Companies Leading the Charge
As the world increasingly pivots towards sustainable energy sources, geothermal energy has gained significant traction.
Several countries and companies have emerged as major investors, driving innovation and expanding the reach of geothermal projects.
Here is an overview of the key players in the global geothermal energy landscape:
1. Iceland: A Pioneer in Geothermal Development
Iceland stands out as a global leader in geothermal energy.
The country, situated on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, harnesses its abundant geothermal resources for both electricity generation and direct-use applications.
Nearly 90% of Icelandic households benefit from geothermal heating.
And the country’s commitment to renewable energy makes it a frontrunner in the field.
2. United States: Unleashing Geothermal Potential
The United States boasts a diverse geothermal portfolio, with significant investments in states such as California, Nevada, and Oregon.
The U.S. leads the world in installed geothermal capacity, and projects like The Geysers in California.
Operated by Calpine Corporation, exemplify the country’s commitment to expanding geothermal energy production.
3. New Zealand: Tapping into Earth’s Heat
New Zealand is another nation making substantial investments in geothermal energy. The Wairakei Power Station.
Commissioned in 1958, was one of the world’s first major geothermal power plants.
Today, companies like Contact Energy and Mercury Energy continue to play a pivotal role in advancing geothermal technology in the country.
4. Kenya: African Trailblazer in Geothermal
In Africa, Kenya has emerged as a trailblazer in geothermal energy. The East African Rift System provides a geologically favorable environment for geothermal projects.
The Olkaria Geothermal Plant, operated by KenGen (Kenya Electricity Generating Company).
Is Africa’s largest geothermal power station and a testament to Kenya’s commitment to renewable energy.
5. Philippines: Geothermal Powerhouse in Asia
The Philippines ranks among the top geothermal energy producers in Asia.
With active geothermal fields like Tiwi and Mak-Ban, the country harnesses its geothermal potential for electricity generation.
Energy Development Corporation (EDC) is a key player, operating multiple geothermal projects in the Philippines.
6. Ormat Technologies: A Global Geothermal Solutions Provider
Ormat Technologies, a multinational company based in the United States, is a major player in the geothermal industry.
It specializes in designing, developing, and operating geothermal power plants worldwide.
Ormat has been involved in projects in various countries, contributing to the global growth of geothermal energy.
7. Enel Green Power: A Global Renewable Giant
Enel Green Power, an Italian renewable energy company, has a significant presence in the geothermal sector.
With operations in multiple countries, including Italy, the United States, and Chile, Enel is committed to expanding its geothermal portfolio and promoting sustainable energy practices.
As the demand for clean and sustainable energy intensifies, these countries and companies are at the forefront of unlocking the Earth’s heat for power generation.
Showcasing the global commitment to a greener and more sustainable energy future.
The ongoing investments and advancements in geothermal technology underscore its potential to play a crucial role in the global energy transition.
Unlocking Opportunities: Investing in the Geothermal Energy Revolution
As the world seeks to transition towards sustainable energy sources, geothermal energy presents compelling investment opportunities.

The unique advantages of geothermal power, coupled with advancements in technology and a global push for renewable energy, make this sector increasingly attractive for investors.
Here’s a comprehensive exploration of the investment landscape in geothermal energy:
**1. Stable and Predictable Returns:
Geothermal power plants offer investors a stable and predictable source of returns. Unlike some renewable sources such as solar and wind, geothermal energy is not weather-dependent.
The Earth’s heat is a continuous and reliable resource, providing a consistent stream of electricity, making it an appealing option for long-term investments.
**2. Government Incentives and Policies:
Many governments worldwide are promoting investments in renewable energy, including geothermal.
Investors can benefit from various incentives, tax credits, and favorable policies designed to accelerate the growth of geothermal projects.
By aligning investments with these incentives, stakeholders can enhance their overall returns and mitigate risks.
**3. Technological Advancements:
Ongoing advancements in geothermal technology are opening new frontiers for investment.
Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS) and innovative drilling techniques are expanding the reach of geothermal resources, making previously untapped areas viable for development.
Investors looking for opportunities at the cutting edge of technology may find the geothermal sector particularly appealing.
**4. Global Expansion and Emerging Markets:
While traditional geothermal powerhouses like Iceland and the United States continue to lead, emerging markets are increasingly recognizing the potential of the geothermal energy.
Investors can explore opportunities in countries with untapped geothermal potential, such as those in Africa, Latin America, and Asia.

These regions offer a growing market for the geothermal projects, presenting early-entry opportunities for investors.
**5. Diversification within Renewable Energy:
Geothermal energy provides investors with a valuable diversification option within the broader renewable energy sector.
By including geothermal projects in a portfolio, investors can balance risks associated with other renewable sources like solar and wind, which are subject to intermittent availability and weather patterns.
**6. Infrastructure Investments:
Investing in geothermal energy involves not only the development of power plants but also the necessary infrastructure such as transmission lines and distribution networks.
This presents additional investment opportunities for those looking to support the overall growth of the geothermal energy sector.
**7. Environmental and Social Impact Investing:
Geothermal energy aligns closely with environmental and social impact goals.
Investors with a focus on sustainability and responsible investing can leverage geothermal projects to contribute to reducing carbon emissions and promoting cleaner energy alternatives.
**8. Mergers and Acquisitions:
As the geothermal energy industry matures, there may be opportunities for mergers and acquisitions.
Companies with expertise in geothermal exploration, development, or technology may become targets for larger energy corporations seeking to diversify their renewable energy portfolios.
The geothermal energy sector is poised for substantial growth, offering investors a range of opportunities across various aspects of the value chain.
From direct investments in power plants to supporting infrastructure development and exploring emerging markets,
The geothermal energy revolution presents a compelling case for those seeking sustainable and impactful investment opportunities.
As the world continues its shift towards cleaner energy, geothermal investments stand at the forefront of the renewable energy transition.

Conclusion:
Geothermal Energy — A Pinnacle in Earth’s Bounty Unveiled
In the tapestry of renewable energy, where innovation intertwines with sustainability, geothermal energy stands as a resolute beacon.
Unveiling the extraordinary potential nestled within the Earth’s embrace.
The journey through the exploration of harnessing the Earth’s heat has unearthed not merely a source of power.
But a transformative force shaping the very contours of our energy landscape.
As we navigate the complexities of a world riddled with environmental challenges, geothermal energy emerges as a cornerstone in the edifice of solutions.
Its inherent virtues — reliability, sustainability, and minimal environmental impact — position it as a protagonist in the epic narrative of the global energy transition.
The Earth’s heat, once a latent force beneath our feet, has now become a dynamic catalyst for change.
Steering us away from the shackles of fossil fuel dependency towards a future powered by ingenuity and environmental responsibility.
The symbiotic dance between technology and nature has birthed a myriad of methodologies to tap into this clandestine reservoir of energy.
From the rhythmic churning of binary cycle power plants to the direct communion with the Earth’s warmth in direct-use applications.

The marriage of human innovation and the planet’s bounty is nothing short of poetic.
The depths to which we drill, the fluids we circulate, and the turbines we set in motion — each action reverberates as a testament to our ability to coalesce with nature for the greater good.
Examining the global stage, we witness nations — be it the pioneering strides of Iceland, the vast geothermal fields of Kenya,
Or the ongoing commitment of the United States — collectively embracing the promise of geothermal energy.
These nations are not merely investors in a power source; they are stewards of a sustainable future, custodians of an energy revolution echoing through the corridors of time.
On the corporate frontier, companies like Ormat Technologies and Enel Green Power have taken up the mantle of progress, becoming architects of geothermal solutions.
Their endeavors transcend profit margins; they are architects of a legacy, weaving a narrative where profitability converges with environmental stewardship.
The investment opportunities in the geothermal energy industry present a symphony of possibilities for those seeking not just financial returns but a chance to be architects of change.
Governments across the globe, cognizant of the imperative to transition towards cleaner energy.
Have unfurled incentives and policies, creating a fertile ground for financial cultivation in the geothermal terrain.
The dividends, however, are not just monetary; they are dividends paid in reduced carbon footprints.
In cleaner air, and in the promise of a sustainable future for generations to come.
In conclusion, the unveiling of the geothermal energy represents a paradigm shift in our approach to power generation.
It is a narrative of harmony — a harmonious partnership between humanity and the Earth, between progress and responsibility.
As we stand at the cusp of a new era, the geothermal energy revelation beckons us to imagine a world where our energy needs are met without compromising the very essence of our planet.
The Earth’s heat, once relegated to the realm of natural phenomena, now emerges as a cornerstone in the human quest for a sustainable and harmonious coexistence with our planet.
In the unveiling of geothermal energy, we find not just a solution to our energy needs but a profound revelation of our ability to forge a future where progress and preservation walk hand in hand.





Leave a Reply